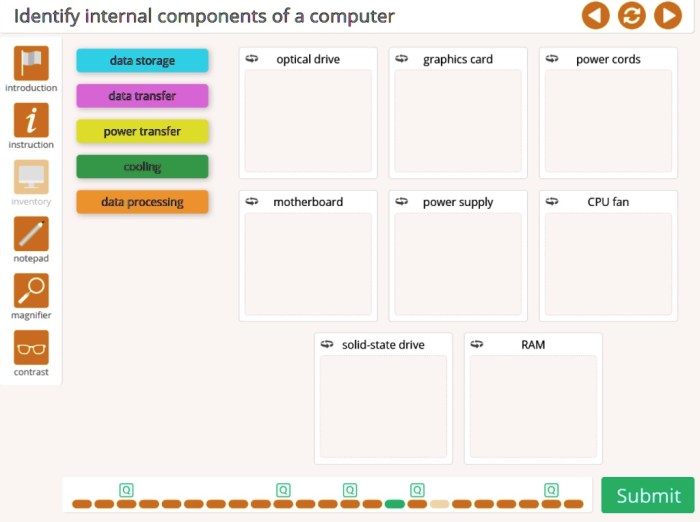
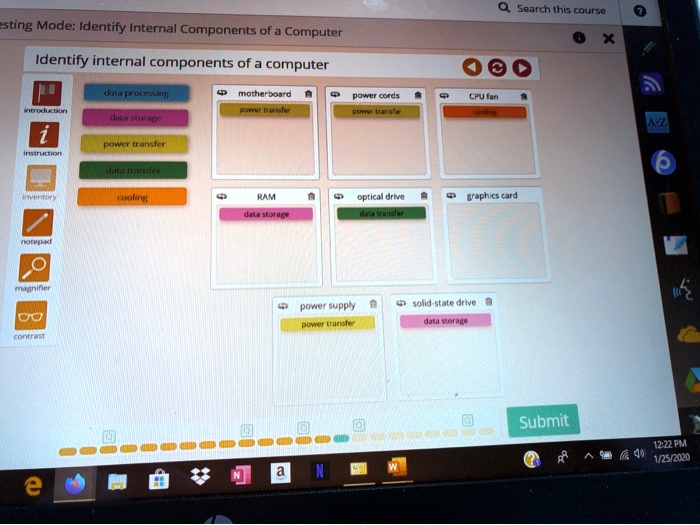
Lab 1-3 testing mode identify internal components of a computer is an essential tool for computer technicians and enthusiasts alike. By entering this mode, users can gain a comprehensive understanding of a computer’s internal components, their functions, and how they work together to form a functional system.
This knowledge is crucial for troubleshooting, optimizing, and upgrading computer systems.
This guide will provide a detailed overview of Lab 1-3 testing mode, including its purpose, objectives, and procedures. We will also explore the diagnostic capabilities and limitations of this mode and discuss how it can be used to identify and resolve common internal component failures.
Additionally, we will provide guidance on optimizing system performance through component upgrades and discuss the potential benefits and limitations of such upgrades.
Internal Components Identification: Lab 1-3 Testing Mode Identify Internal Components Of A Computer
A computer’s internal components are essential for its functioning. These components include the following:
- Processor (CPU):The brain of the computer, responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations.
- Memory (RAM):Stores temporary data and instructions being processed by the CPU.
- Storage (HDD/SSD):Stores data permanently, such as the operating system, programs, and files.
- Graphics Card (GPU):Processes and renders visual data for display on the monitor.
- Sound Card:Processes and generates sound for speakers or headphones.
- Network Adapter:Connects the computer to a network for internet access and data transfer.
- Motherboard:The central hub that connects all other components and facilitates communication between them.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU):Provides electrical power to all components.
- Cooling System:Keeps the components within safe operating temperatures.
Lab 1-3 Testing Mode
Lab 1-3 testing mode is a diagnostic tool that allows technicians to test the functionality of a computer’s hardware components.
Procedures:
- Enter the BIOS settings during boot.
- Navigate to the “Testing” or “Diagnostics” section.
- Select the desired test (e.g., memory, storage, etc.).
- Run the test and observe the results.
Capabilities:
- Identify faulty components.
- Verify the integrity of hardware.
- Assist in troubleshooting and repair.
Limitations:
- Cannot detect all types of hardware failures.
- May not provide specific error codes.
- Does not repair or fix hardware issues.
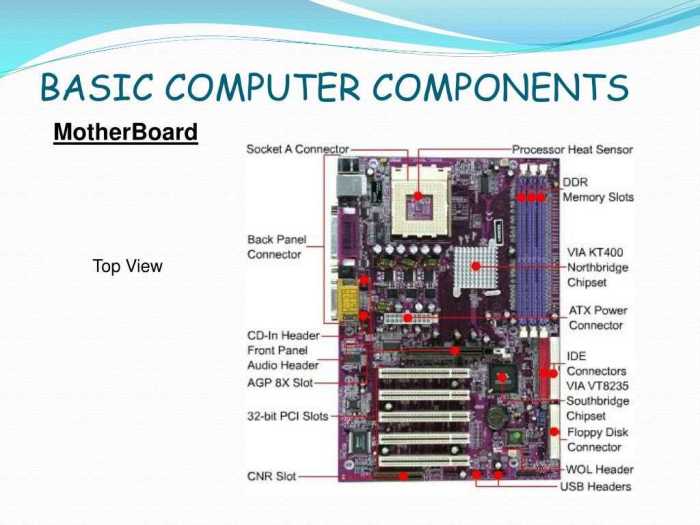
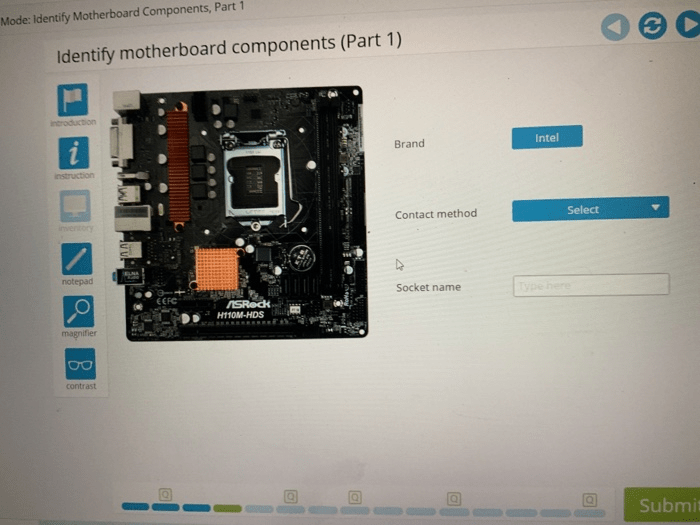
Motherboard Analysis, Lab 1-3 testing mode identify internal components of a computer
The motherboard is the backbone of a computer, connecting and coordinating all its components.
Key Components:
- CPU Socket:Accommodates the processor.
- Memory Slots:Hold RAM modules.
- Expansion Slots:Allow the installation of additional components (e.g., graphics cards).
- BIOS Chip:Stores firmware that initializes the computer.
- Southbridge Chipset:Controls peripheral devices (e.g., USB, SATA).
- Northbridge Chipset:Connects the CPU to the memory and graphics card.
Functions:
- Provides power to components.
- Facilitates communication between components.
- Controls system settings and configuration.
Troubleshooting Internal Components
Common internal component failures and troubleshooting steps:
- Processor (CPU):Overheating, check cooling system. Corrupted firmware, update BIOS.
- Memory (RAM):Loose or faulty modules, reseat or replace. Damaged memory cells, run memory diagnostic tests.
- Storage (HDD/SSD):Mechanical failure, listen for clicking sounds. Data corruption, run disk repair tools.
- Graphics Card (GPU):Overheating, check cooling system. Driver issues, update drivers.
- Sound Card:Loose connections, check cables. Damaged card, replace.
- Network Adapter:Faulty cable or port, replace. Driver issues, update drivers.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU):Overloaded or underpowered, check power draw. Damaged components, replace.
Advanced Component Analysis
Specialized components enhance computer capabilities:
- Graphics Cards (GPUs):Handle complex graphics processing, essential for gaming and video editing.
- Sound Cards:Provide high-quality audio for music production and surround sound.
- Network Adapters:Enable fast and stable internet connections, including Wi-Fi and Ethernet.
Considerations:
- Performance:Measured in clock speed, memory capacity, and bandwidth.
- Compatibility:Ensure components are compatible with the motherboard and other hardware.
- Budget:Advanced components can be expensive.
System Optimization and Upgrades
Enhance system performance through component upgrades:
- Upgrade CPU:Increase processing power for demanding tasks.
- Add RAM:Improve multitasking and application responsiveness.
- Replace HDD with SSD:Accelerate boot times and application loading.
- Install a Graphics Card:Enhance graphics capabilities for gaming and video editing.
Considerations:
- Compatibility:Ensure upgrades are compatible with existing hardware.
- Budget:Upgrades can be expensive.
- Cooling:High-performance components may require additional cooling.
Clarifying Questions
What is the purpose of Lab 1-3 testing mode?
Lab 1-3 testing mode is designed to provide users with a comprehensive overview of a computer’s internal components, their functions, and how they work together to form a functional system.
How do I enter Lab 1-3 testing mode?
The specific procedure for entering Lab 1-3 testing mode may vary depending on the computer system. Generally, it involves restarting the computer and pressing a specific key or key combination during the boot process.
What are the diagnostic capabilities of Lab 1-3 testing mode?
Lab 1-3 testing mode provides a range of diagnostic capabilities, including the ability to test individual components, such as memory, storage, and peripherals. It can also be used to identify and resolve common hardware conflicts and errors.
What are the limitations of Lab 1-3 testing mode?
Lab 1-3 testing mode is primarily designed for basic hardware diagnostics and troubleshooting. It may not be able to detect or resolve all types of computer problems, especially those related to software or operating system issues.
How can I use Lab 1-3 testing mode to troubleshoot computer problems?
By following the step-by-step procedures provided in Lab 1-3 testing mode, users can isolate and identify the source of common hardware problems. This information can then be used to resolve the issue or determine if further professional assistance is required.